Resistant materials in the aerospace industry

TANIOBIS develops pioneering niobium alloys for NewSpace
Europe’s space ambitions are gathering momentum, with a key material garnering close increasing attention in the aerospace industry: niobium. With niobium-based alloy powders, TANIOBIS GmbH is delivering solutions that meet the rising demands of aerospace systems, thus positioning itself as a driving force in the emerging European NewSpace market.
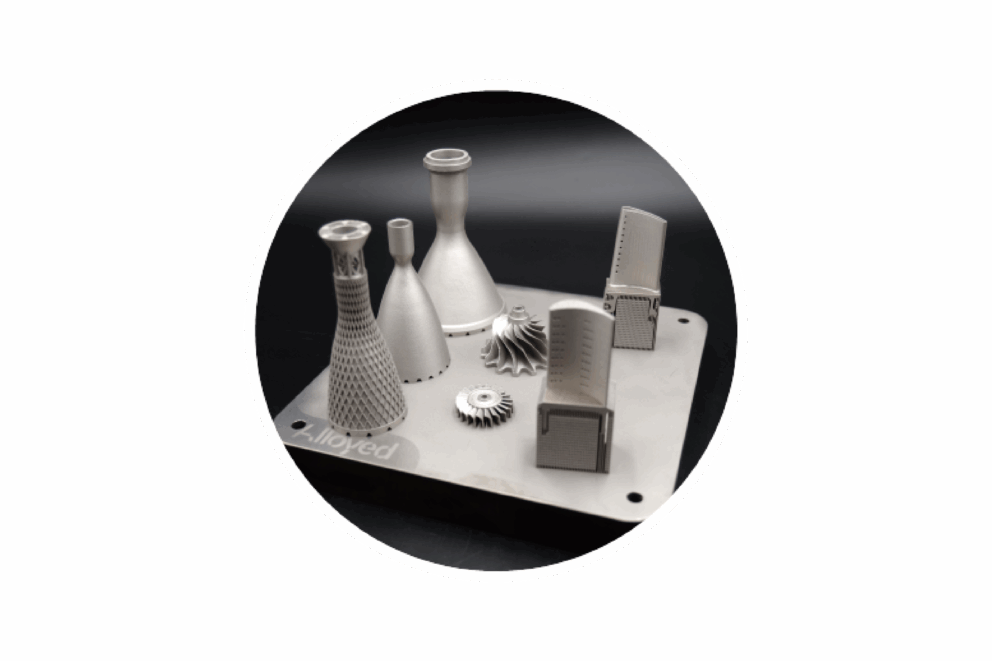
TANIOBIS has a long-standing track record in developing tailor-made alloy powders based on niobium, such as AMtrinsic® C-103 and AMtrinsic® FS-85, both used in additive manufacturing. These alloys stand out due to their strength at temperatures above 1000 °C, and are ideally suited for manufacturing demanding components such as jet engine nozzles, control segments, and satellite thrusters. These materials are already in use wherever structural components must perform reliably under extreme temperature conditions.
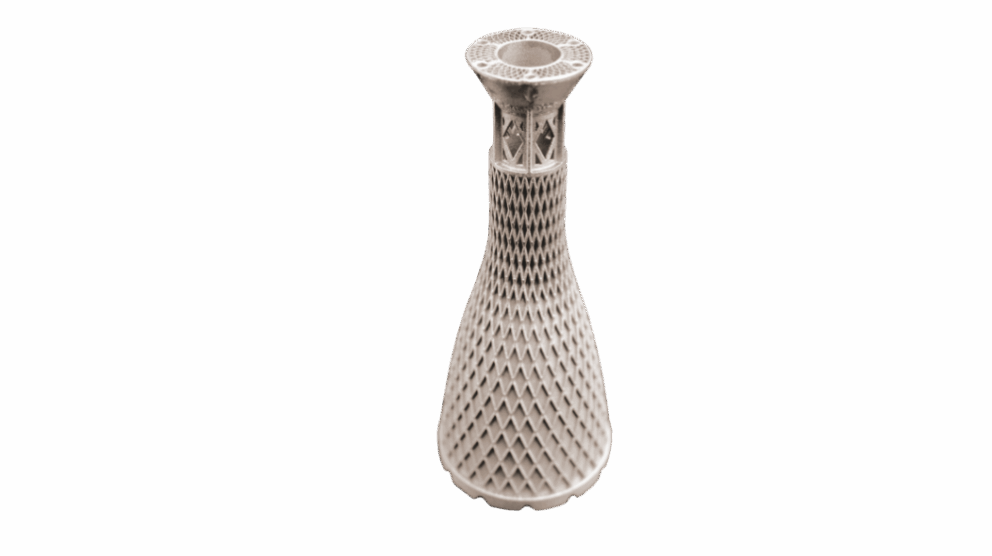
The demand for materials with high-temperature resistance has surged in the aerospace industry over recent years. However, conventional nickel-based alloys reach their mechanical stability limit at around 1050 °C. Niobium-based metal alloys significantly outperform them in this respect. Thanks to additive manufacturing, AMtrinsic® alloy powders enable the production of complex, geometry-optimized components which are difficult or even impossible to achieve using conventional methods.
Manufacturing heat-resistant components for aerospace application imposes stringent requirements on both materials and manufacturing process. This is precisely where TANIOBIS excels. Its powders have been continuously developed in close cooperation with relevant research institutions and international companies to actively help define the next stage of technological advancement in aerospace technology.

Resisting extreme thermal loads
A current NASA research project shows how important niobium alloys are for precisely this type of application. NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland additively manufactured different niobium alloys, including C-103, FS-85 and Cb-752, and examined their mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. The results showed that FS-85 and Cb-752 outperform C-103 in respect of mechanical strength as well as creep performance at high temperatures. These results highlight the advantage of these less common niobium alloys and their potential for use in demanding aerospace environments such as thermal protection components or thermally stressed areas of propulsion systems. “Our AM alloys are specifically engineered to meet such challenging requirements,” affirmed Dr. Bahar Fayyazi, Product Manager at TANIOBIS. “From precise satellite thrusters through to reusable space launch systems, niobium alloys combine high-temperature stability with mechanical integrity, thus offering a material base for new space missions.”
With its 3D-printable niobium alloys, TANIOBIS is helping to reinforce and expand the material foundation for next-generation European aerospace technologies. These precisely engineered powders enable additive manufacturing with minimal material waste, high geometrical complexity, and consistent material properties. In this way, TANIOBIS is actively laying the foundation for sustainable space development in Europe.